# Project Resolution
It's best practice to prepare your main background image with a photo editor of your choice to ensure that the wallpaper uses a resolution that exists on computer monitors. Strictly speaking, this is not necessary and Wallpaper Engine will accept any image resolution, however, you will achieve the best performance if the wallpaper matches the resolution of your screen or at least the correct aspect ratio.
The most common resolutions are 1920x1080 ("Full HD") and 3840x2160 ("4K UHD"). If your wallpaper does not use a resolution from the supported resolution list, it will be marked as Other Resolution which may negatively affect its popularity.
Click here to view all official resolutions
The following resolutions were selected based on the most common resolutions on the market:
16:9
- 1280 x 720
- 1366 x 768
- 1920 x 1080
- 2560 x 1440
- 3840 x 2160
Two screens or one ultrawide screen
- 2560 x 1080 (Ultrawide)
- 3440 x 1440 (Ultrawide)
- 3840 x 1080 (2x Full HD or 1x Ultrawide)
- 5120 x 1440 (2x 1440p or 1x Ultrawide)
- 7680 x 2160 (2x 4K UHD)
Triple screens
- 4096 x 768 (3x 768p)
- 5760 x 1080 (3x Full HD)
- 7680 x 1440 (3x 1440p)
- 11520 x 2160 (3x 4K UHD)
Portrait aspect ratios (screen turned by 90°)
- 720 x 1280 (Portrait 9:16)
- 1080 x 1920 (Portrait 9:16)
- 1440 x 2560 (Portrait 9:16)
- 2160 x 3840 (Portrait 9:16)
To exemplify why it's bad to use wallpapers that do not have a real aspect ratio: Let's say you have an image that is 2000x2000 pixels. No computer monitor on the market has this resolution, so when you import and animate an image with this resolution, Wallpaper Engine will cut off the sides of your wallpaper once you apply it to your desktop to make it fit to your screen. The following image showcases how much is cut off if you use a 2000x2000 image on a 1920x1080 monitor:
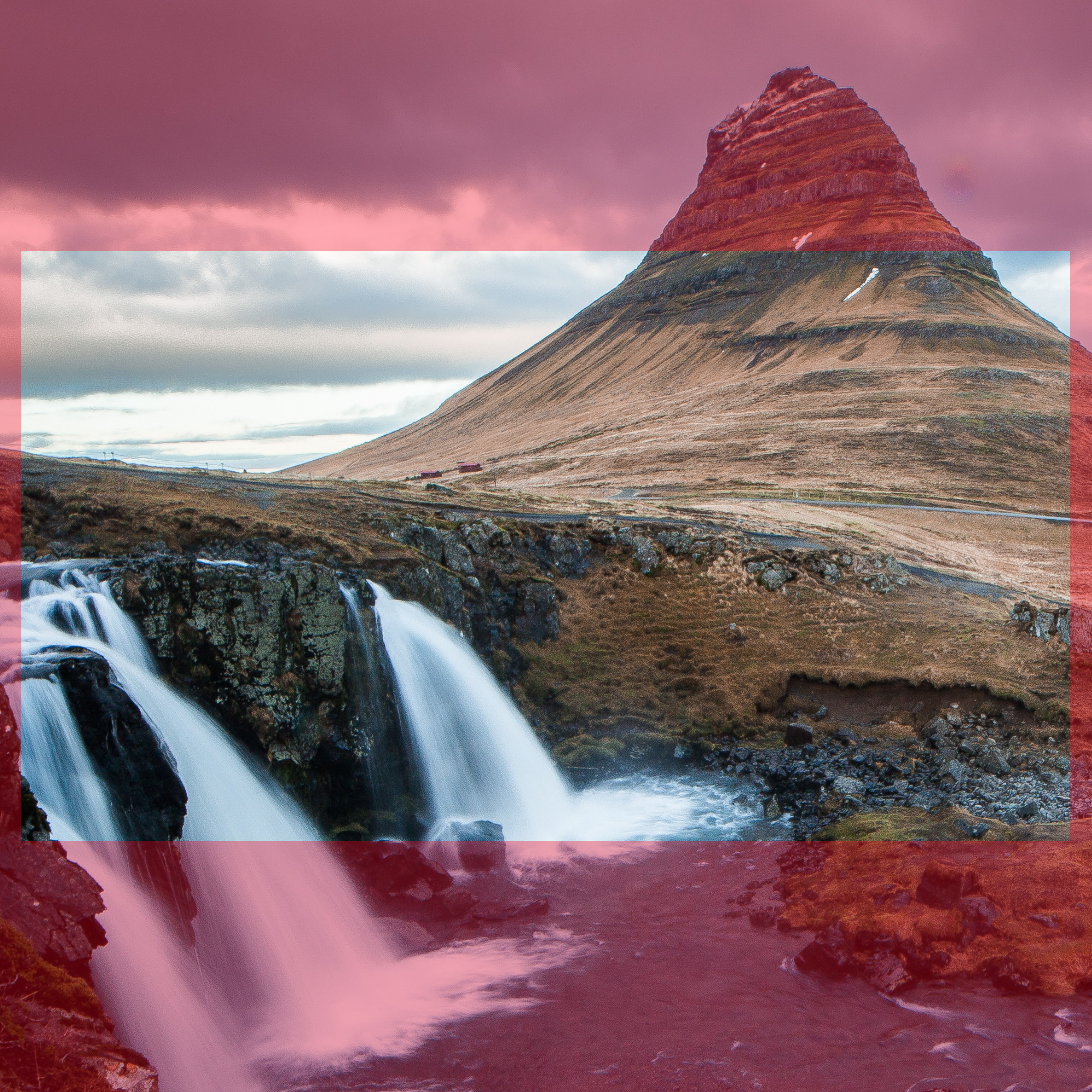 Red areas are cut off if this square image was displayed on a 16:9 monitor.
Red areas are cut off if this square image was displayed on a 16:9 monitor.
The downsides of this are an increased graphics card usage, less control over what is actually visible on the screen and larger file sizes. This also applies to any image layers you use - they should all be as small as possible.
We generally recommend you scale down images to the closest real resolution and then manually crop off excess areas. You can use free image editing tools like Microsoft Paint, Paint.NET, GIMP or paid alternatives such as Adobe Photoshop to do this. Again, it's not necessary but we recommend preparing background images before importing them.